SilverStone Argon Cooler Round Up
Author: Dennis GarciaBenchmarks
The SilverStone Argon AR07 and AR08 are designed to fit Intel Socket LGA2011 / 1156 / 1155 / 1150 and AMD processors. Here is an overview of the system and testing methodology.
Asus P8Z68 Deluze Gen3 Intel Z68 Chipset
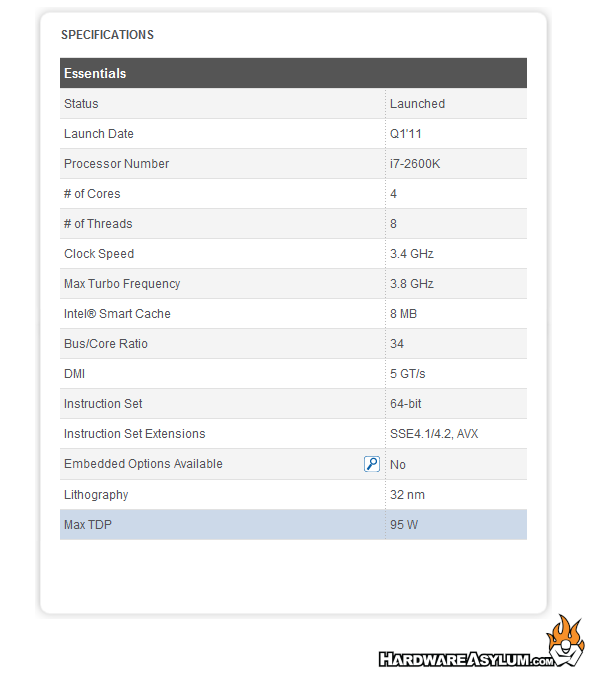
Intel Core i7 2600K (3.5Ghz) Quad Core 4 x 256KB L2 Cache 8MB L3 Cache
SilverStone Argon SST-AR06
SilverStone Argon SST-AR07
SilverStone Argon SST-AR08
Intel OEM Heatsink
The CPUID System Monitor was used to obtain and record system temperature data and being that this is a quad core processor we need something that will work across all of the cores at once. For this task we're using a new version of Prime95 (p95v255a) that will allow you to spawn (n) instances to test with.
Editors note: Even though the Windows 7 task manager reported 100% processor usage we could never attain a 100% of the rated heat output as documented by Intel (see below) when using Prime95 as a basis for that heat production. Knowing this we ran the stress test until the maximum temperature was attainted and stabilized.
Other things to consider when judging software induced heat output.
a) Clock throttling by the processor at high temperatures.
b) Normal software isn't designed to produce maximum heat output.
c) Variances of cooling temperature.
d) Variances in CPU load.
e) Inaccuracies in thermal diode readouts.
Of course the list goes on..
Our testing methodology is aimed to provide a real world look into this heatsink given the test system provided.
A C/W rating can quickly be calculated using this formula.
C/W = (CPU temp - Ambient temp)/(Variance(%) * CPU Watts)
Allowed variance for this test = 85%
CPU Watts = 95W
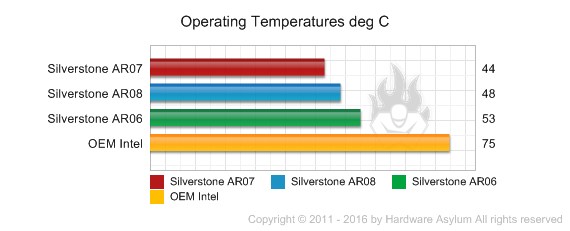
SST-AR07 - 0.22 C/W = (44C - 26C)/(.85(95W))
SST-AR08 - 0.27 C/W = (48C - 26C)/(.85(95W))
SST-AR06 - 0.33 C/W = (53C - 26C)/(.85(95W))
For this next test the CPU speed was cranked up to 4.5Ghz and the test was re-run.

ocC/W = dCPU Watts * (ocMhz / dMhz) * (ocVcore / dVcore)2
ocMhz = 4500
dMhz = 3500
ocVcore = 1.3
dVcore = 1.2
The variance still applies for our C/W calculation
Allowed variance for this test = 85%
CPU Watts = 143W
SST-AR07 - 0.25 C/W = (56C - 26C)/(.85(143W))
SST-AR08 - 0.32 C/W = (65C - 26C)/(.85(143W))
In our heatsink and waterblock tests we don't really focus on overall load temperatures but rather how well the product can remove heat given a specified heat load. Since this is a real world testing method we need to take into consideration real world variables and estimate tolerances. This is why we normally only apply 85% of the total wattage output to our heat calculations.
The resulting C/W number is used to rate how efficient a heatsink or waterblock is based on the given heat load. These numbers can be used to determine heat capacity, the larger the difference the less efficient the heatsink is. (aka not good for overclocking)
The charts show an interesting progression. At the default speed we see how the SST-AR07 is working the way you would expect a 140mm tower should with only a minor performance drop from the SST-AR08 with its smaller 92mm fan. The low profile SST-AR06 is also doing quite well besting the OEM cooler by 20 degrees!
In terms of performance the C/W numbers are what we are expecting with about 0.05 C/W difference between heatsinks. Moving into the overclocking tests the charts illustrate how quickly a few extra watts can saturate a core contact heatsink. The SST-AR07 is still doing quite well with only a 0.03 C/W change while the smaller SST-AR08 begins to struggle.
For the record the SST-AR07 starts to saturate around the 4.7Ghz level with 167W.
It should also be noted that we did test this heatsink using all fans spinning under the Asus Turbo PWM fan profile. This profile is a little more aggressive than the default enabling them to spin up faster under load.
Keep in mind these calculations are provided for demonstration purposes only and may not reflect the actual lab tested C/W rating, but we're pretty close.

