Asus P8P67 Evo Motherboard Review
Author: Dennis Garcia
Published: Monday, April 25, 2011
Board Layout and Features Cont.
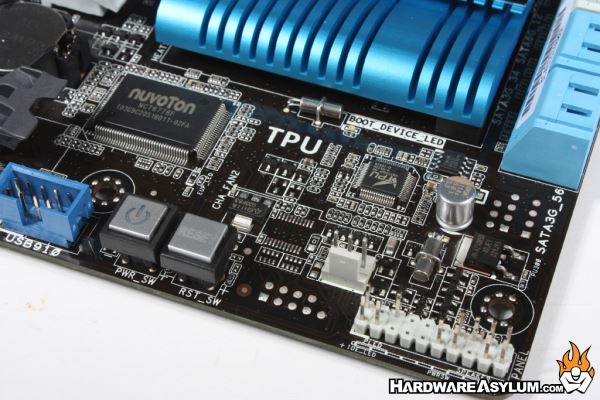
When using any system outside of a chassis it is nice to have onboard buttons available to power and reset the system without shorting pins on the front panel connector. Both buttons are backlit when there is power available thus making them easy to spot with the lights down. In the background you'll see an extremely small processor just below the MCP heatsink. This chip is the TPU processor that controls the auto power up features and TurboV EVO software overclocking package.
TPU and EPU
To enable the TPU feature you must first enable the hardware switch located under the last PCI Express slot. Once enabled the system will auto tune your processor and memory combo for the best performance short of a manual overclock.
Another onboard hardware switch is called EPU. The EPU system is a real time power saving feature that looks at system load and will adjust power delivery dynamically and moderate power consumption. While these switches appear to do completely different things you can use them at the same time and still expect full system performance when you need it most.
The I/O panel is rather self explanatory. On the panel you will find two PS/2 ports for keyboard and mouse connections. Digital audio, Bluetooth ( 2.1+EDR ), eSATA, Firewire, USB (both 2.0 and 3.0 standards) dual Ethernet with one being controlled by an Intel Gigabit Phy, CMOS reset and 8-channel analog audio.
The I/O panel is rather self explanatory. On the panel you will find two PS/2 ports for keyboard and mouse connections. Digital audio, Bluetooth ( 2.1+EDR ), eSATA, Firewire, USB (both 2.0 and 3.0 standards) dual Ethernet with one being controlled by an Intel Gigabit Phy, CMOS reset and 8-channel analog audio.
Internal SATA connections number eight. The light blue connections are SATA3 spec while the white connections follow the SATA6 connections standard direct from the P67 chipset. The remainder dark blue SATA ports are SATA6 compliant and are provided by the onboard Marvell controller.
You may have noticed a single BIOS chip located near the SATA connections and below the internal USB3 panel connector. The P8P67 Evo features a single BIOS chip but is removable in the event of a failed BIOS flash or BIOS corruption.
You may have noticed a single BIOS chip located near the SATA connections and below the internal USB3 panel connector. The P8P67 Evo features a single BIOS chip but is removable in the event of a failed BIOS flash or BIOS corruption.